Pediatric pyoderma gangrenosum associated with Crohn's disease successfully treated with adalimumab. Case report and literature review.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.32.1.2304How to Cite
Abstract
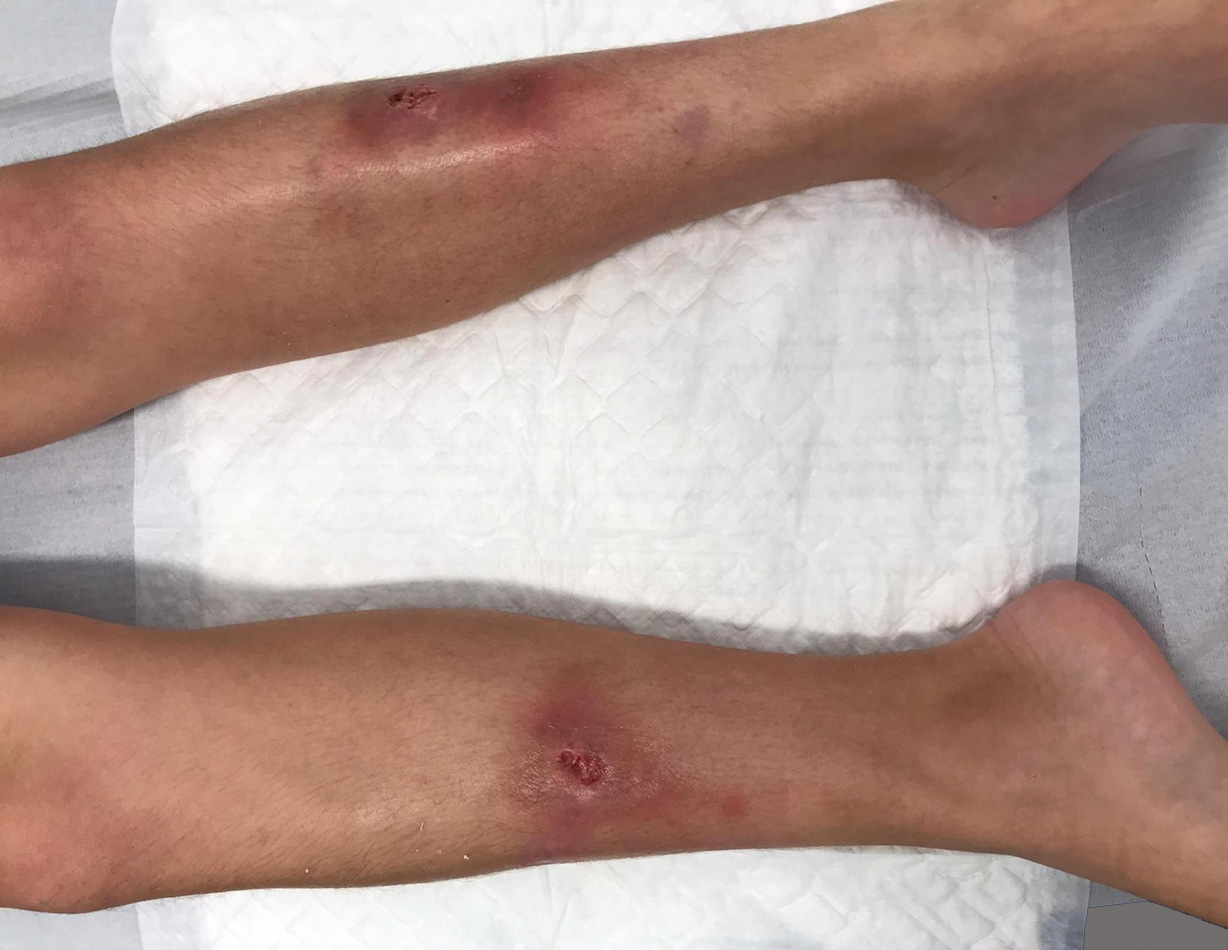
Pyoderma gangrenosum is a rare neutrophilic ulcerative skin disorder that presents a therapeutic challenge. Only 4% of the cases occur in children, most frequently associated with underlying diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease. Recently, tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors were reported to be effective for pyoderma gangrenosum; however, data on their use in pediatric patients remain sparse. We present a case of a 12-year-old boy with ulcerative pyoderma gangrenosum associated with ileocolic Crohn’s disease successfully treated with adalimumab. Skin lesions healed completely after five weeks of treatment. In addition, we review previous reports of the use of tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors to treat pediatric pyoderma gangrenosum.
