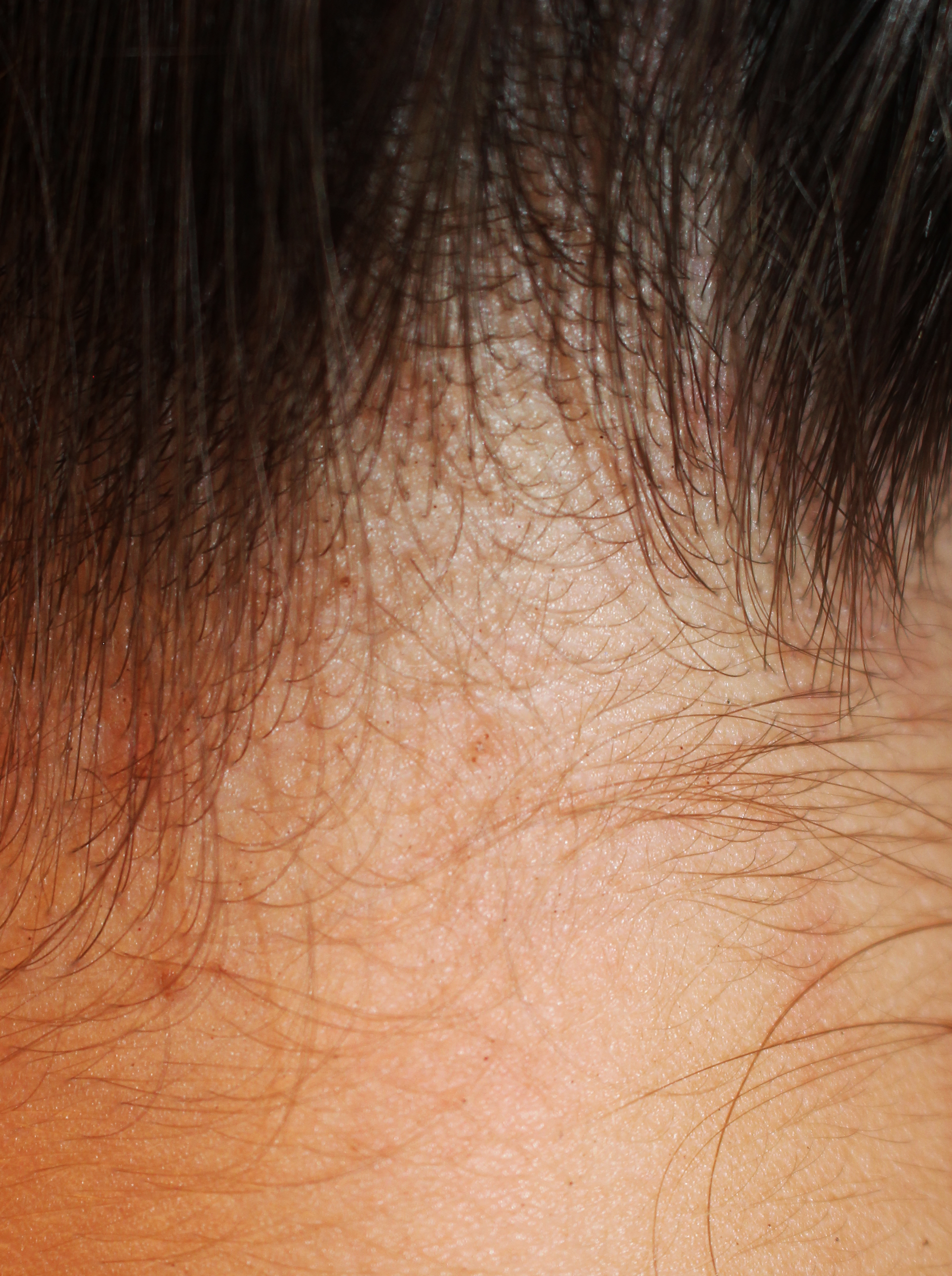
Familial phthiriasis of the hairline.
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26326/2281-9649.28.3.1889How to Cite
Abstract
In the prepubescent child, the infestation usually takes place by sleeping in the same bed with an affected relative or by sharing towels or wipes infested with the parasite. Unlike the Pediculus capitis, the pubic louse moves little, but certainly moves because we have demonstrated its presence in the vicinity of a macula cerulea (1). The hook shape of the second and third pair of legs allows to cling to the coarse hairs of the pubis, armpit and beard. In the prepubescent child, in the absence of such hairs, the pubic louse chooses eyelashes and hairline, but a case of phthiriasis with involvement of the entire scalp in a 6-week-old child has been described (2).
However, it is the macula cerulea that brings the child to the doctor. The therapy is the same as the pediculosis of the head and the daily use of the nit comb is fundamental until the infestation disappears.
